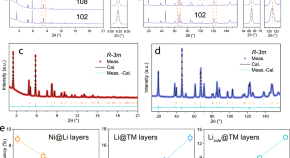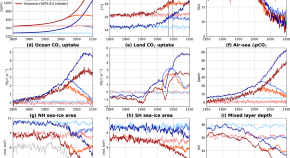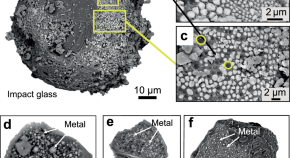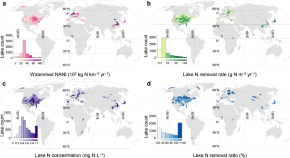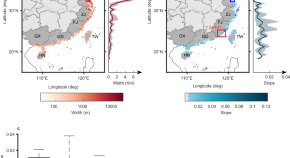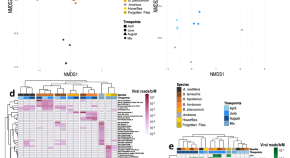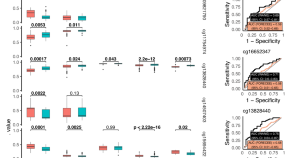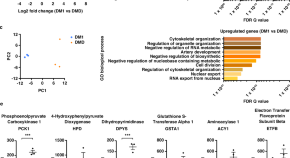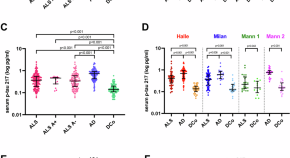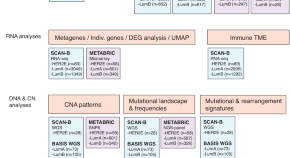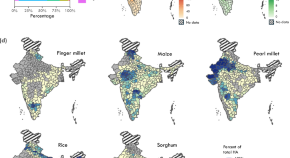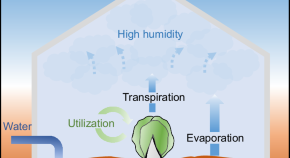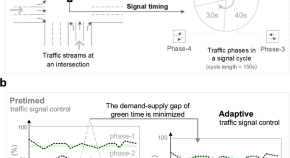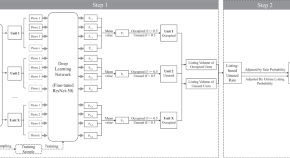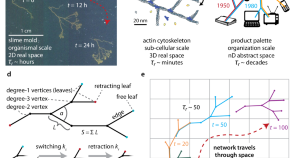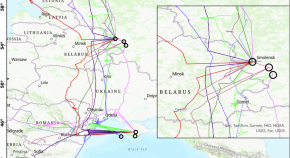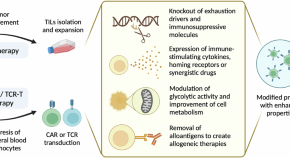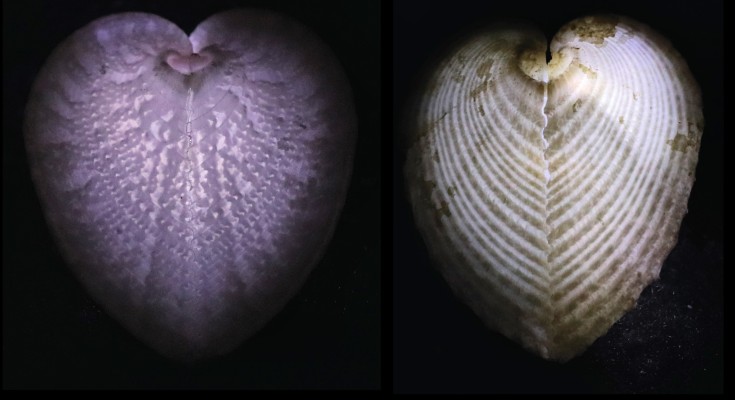
Heart cockle shells transmit sunlight to internal symbiotic algae using mineral optical fibers and lenses
Dakota McCoy et al. show that heart cockles transmit light through their upper shell to internal symbiotic algae using mineral fiber optic cables and lenses to maximize light transmission.