Markets
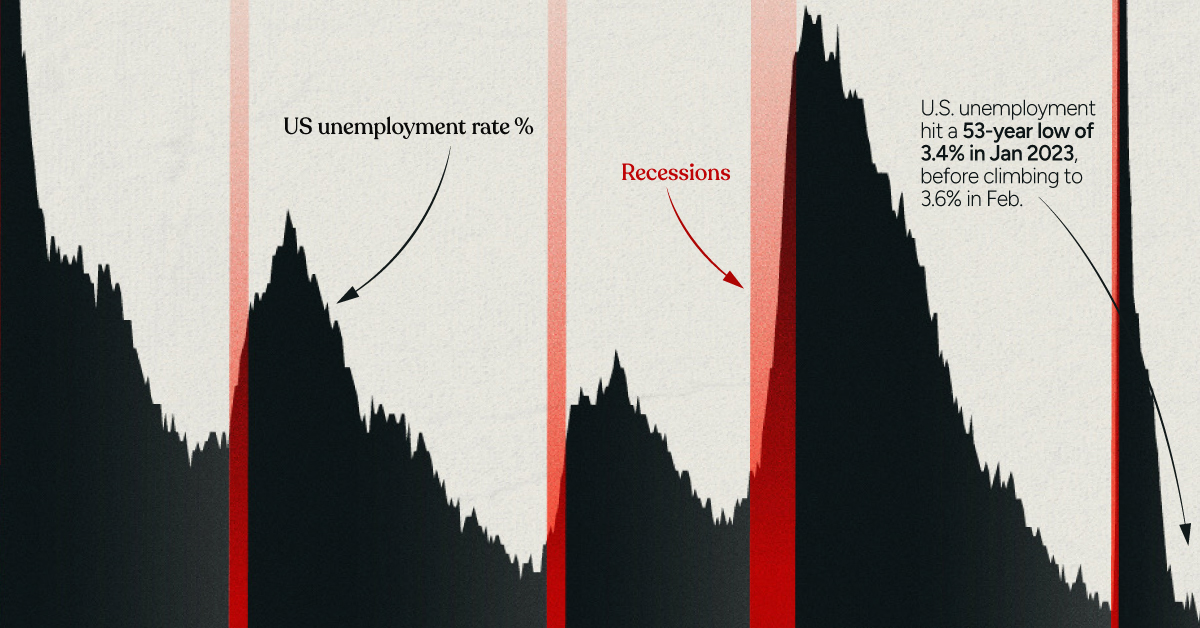
Visualizing the Link Between Unemployment and Recessions
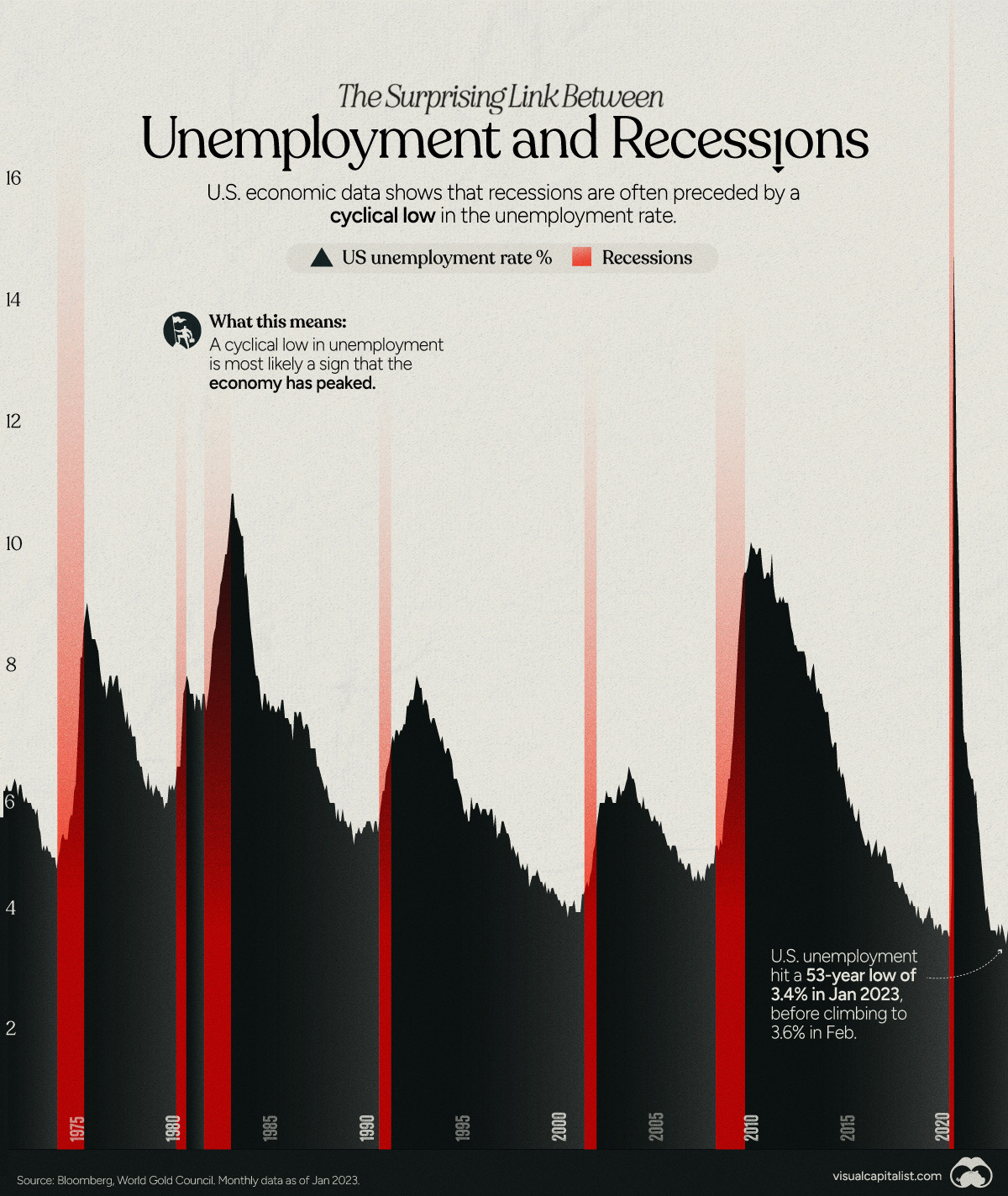
The Surprising Link Between Unemployment and Recessions
The U.S. labor market is having a strong start to 2023, adding 504,000 nonfarm payrolls in January, and 311,000 in February.
Both figures surpassed analyst expectations by a wide margin, and in January, the unemployment rate hit a 53-year low of 3.4%. With the recent release of February’s numbers, unemployment is now reported at a slightly higher 3.6%.
A low unemployment rate is a classic sign of a strong economy. However, as this visualization shows, unemployment often reaches a cyclical low point right before a recession materializes.
Reasons for the Trend
In an interview regarding the January jobs data, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen made a bold statement:
You don’t have a recession when you have 500,000 jobs and the lowest unemployment rate in more than 50 years
While there’s nothing wrong with this assessment, the trend we’ve highlighted suggests that Yellen may need to backtrack in the near future. So why do recessions tend to begin after unemployment bottoms out?
The Economic Cycle
The economic cycle refers to the economy’s natural tendency to fluctuate between periods of growth and recession.
This can be thought of similarly to the four seasons in a year. An economy expands (spring), reaches a peak (summer), begins to contract (fall), then hits a trough (winter).
With this in mind, it’s reasonable to assume that a cyclical low in the unemployment rate (peak employment) is simply a sign that the economy has reached a high point.
Monetary Policy
During periods of low unemployment, employers may have a harder time finding workers. This forces them to offer higher wages, which can contribute to inflation.
For context, consider the labor shortage that emerged following the COVID-19 pandemic. We can see that U.S. wage growth (represented by a three-month moving average) has climbed substantially, and has held above 6% since March 2022.
The Federal Reserve, whose mandate is to ensure price stability, will take measures to prevent inflation from climbing too far. In practice, this involves raising interest rates, which makes borrowing more expensive and dampens economic activity. Companies are less likely to expand, reducing investment and cutting jobs. Consumers, on the other hand, reduce the amount of large purchases they make.
Because of these reactions, some believe that aggressive rate hikes by the Fed can either cause a recession, or make them worse. This is supported by recent research, which found that since 1950, central banks have been unable to slow inflation without a recession occurring shortly after.
Politicians Clash With Economists
The Fed has raised interest rates at an unprecedented pace since March 2022 to combat high inflation.
More recently, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell warned that interest rates could be raised even higher than originally expected if inflation continues above target. Senator Elizabeth Warren expressed concern that this would cost Americans their jobs, and ultimately, cause a recession.
According to the Fed’s own report, if you continue raising interest rates as you plan, unemployment will be 4.6% by the end of the year.
– Elizabeth Warren
Powell remains committed to bringing down inflation, but with the recent failures of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank, some analysts believe there could be a pause coming in interest rate hikes.
Editor’s note: just after publication of this article, it was confirmed that U.S. interest rates were hiked by 25 basis points (bps) by the Federal Reserve.
Maps
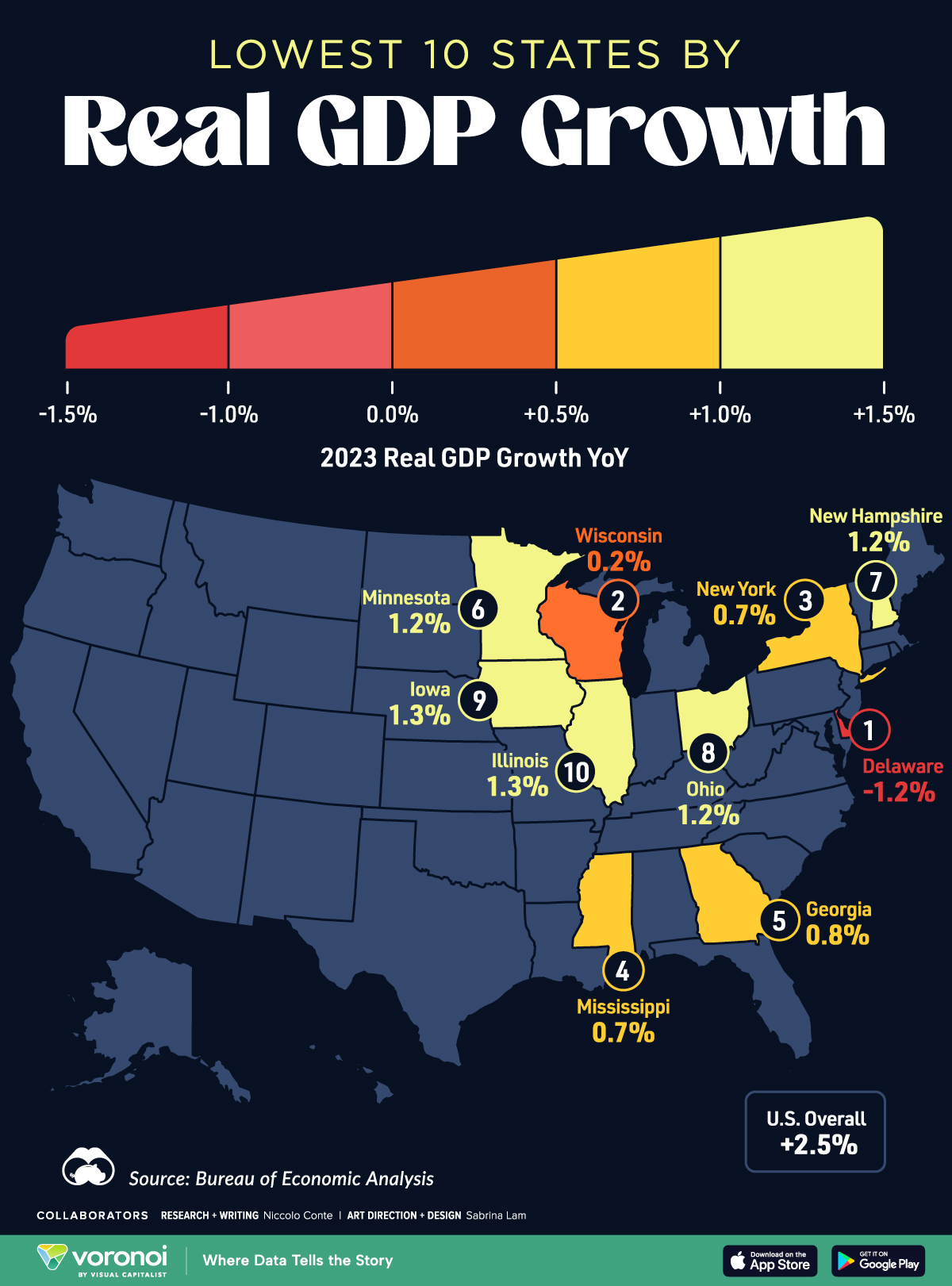
Mapped: The 10 U.S. States With the Lowest Real GDP Growth
In this graphic, we show where real GDP lagged the most across America in 2023 as high interest rates weighed on state economies.

The Top 10 U.S. States, by Lowest Real GDP Growth
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
While the U.S. economy defied expectations in 2023, posting 2.5% in real GDP growth, several states lagged behind.
Last year, oil-producing states led the pack in terms of real GDP growth across America, while the lowest growth was seen in states that were more sensitive to the impact of high interest rates, particularly due to slowdowns in the manufacturing and finance sectors.
This graphic shows the 10 states with the least robust real GDP growth in 2023, based on data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Weakest State Economies in 2023
Below, we show the states with the slowest economic activity in inflation-adjusted terms, using chained 2017 dollars:
| Rank | State | Real GDP Growth 2023 YoY | Real GDP 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delaware | -1.2% | $74B |
| 2 | Wisconsin | +0.2% | $337B |
| 3 | New York | +0.7% | $1.8T |
| 4 | Missississippi | +0.7% | $115B |
| 5 | Georgia | +0.8% | $661B |
| 6 | Minnesota | +1.2% | $384B |
| 7 | New Hampshire | +1.2% | $91B |
| 8 | Ohio | +1.2% | $698B |
| 9 | Iowa | +1.3% | $200B |
| 10 | Illinois | +1.3% | $876B |
| U.S. | +2.5% | $22.4T |
Delaware witnessed the slowest growth in the country, with real GDP growth of -1.2% over the year as a sluggish finance and insurance sector dampened the state’s economy.
Like Delaware, the Midwestern state of Wisconsin also experienced declines across the finance and insurance sector, in addition to steep drops in the agriculture and manufacturing industries.
America’s third-biggest economy, New York, grew just 0.7% in 2023, falling far below the U.S. average. High interest rates took a toll on key sectors, with notable slowdowns in the construction and manufacturing sectors. In addition, falling home prices and a weaker job market contributed to slower economic growth.
Meanwhile, Georgia experienced the fifth-lowest real GDP growth rate. In March 2024, Rivian paused plans to build a $5 billion EV factory in Georgia, which was set to be one of the biggest economic development initiatives in the state in history.
These delays are likely to exacerbate setbacks for the state, however, both Kia and Hyundai have made significant investments in the EV industry, which could help boost Georgia’s manufacturing sector looking ahead.
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoMapped: Countries Where Recreational Cannabis is Legal
-
 Healthcare2 weeks ago
Healthcare2 weeks agoLife Expectancy by Region (1950-2050F)
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Growth of a $1,000 Equity Investment, by Stock Market
-
 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoMapped: Europe’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoCharted: What Frustrates Americans About the Tax System
-
 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoWhere the World’s Aluminum is Smelted, by Country
-

 Personal Finance2 weeks ago
Personal Finance2 weeks agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State